Photovoltaic (PV) generations
The first generation of PV cells was discovered at Bell Telephone in 1954, when scientists discovered that silicon (is one of element found in sand) created an electric charge when exposed to sunlight. Traditional solar cells are made from silicon, one of the most common elements on Earth. Second-generation of PV cells changed names of PV cells into thin film solar cells because they are made from amorphous silicon or non-silicon materials such as Cadmium Telluride Thin film solar cells use layers of semiconductor materials only a few micrometers thick.
The last generation is third-generation solar cells were made from a variety of new materials besides silicon, including solar inks using conventional printing press technologies, solar dyes, and conductive plastics.
Types of Photovoltaic Cells:
There are four types of photovoltaic cells categorized according to silicon crystal and efficient rate and cost of production:
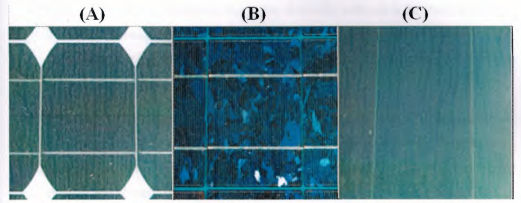
- Monocrystalline silicon(l 5) % efficient, made up of sections of a single silicon crystal. When cooling, the molten silicon solidifies into a single large crystal, typically expensive to make (grown as big crystal).
- Multicrystalline silicon (10-12) % efficient, these are formed by crystallized small particles. During the cooling of the molten silicon, it solidifies creating many crystals. Their appearance is blue too, but it is not uniform, since we can distinguish several different colors created by the glass , cheaper to make (cast in ingots).
- Thin film silicon (4-6) % efficient, cheapest per Watt, easily deposited on a wide range of surface type.
- Amorphous: These cells are produced when the silicon has not yet crystallized during processing, and it produces a gas that is projected onto a glass slide. They are able to operate with low diffuse light, even on cloudy days. The cost is much smaller and it can accommodate both flexible and rigid media. Against this, the performance, in full sunlight conditions, is between (5 -7) %, and it decreases, with the pass of time, around (7) %.
Photovoltaic Applications
Photovoltaic system generates clean electric power, PV provides a suitable energy source for remote regions with no other electricity source. For example, photovoltaic systems can be used to supply electricity for:
- Small scale such as domestic load or a large scale such as grid connected solar powered generator.
- Telecommunication repeater stations using of PV panel to power mobility, radio communication, telephones, remote control systems, emergency call boxes, microwave links, The range of power that is used in these systems varies from a few watts for an emergency call system to several kilowatts for large radio repeaters.
- erospace application used PV panels to supply satellites, space station and telescopes which used in monitoring the space .
- Water pumps: water pumping for irrigation, drinking, and small industrial purposes, this technique especially used in rural areas because, although the electricity is used as it is generated, the water can be stored in tanks during daylight ‘ hours and then using water by gravity when it was needed at night.
- “Village and remote residences: due to the electricity network is far away and the distance between the houses is large although, the number of population is few. The PV system supplies energy effectively for the operation of refrigerators, televisions, lightings, radios, etc.
- Lighting: PV lighting is very common in remote locations such as nature preserves, mountain areas, highway signs, or rural towns and villages, street lighting, security, gardens, vacation cabins, and the car’s sparking, these kinds of lighting systems are reliable and cheap cost.
- Handle electronics devices: One of the uses of PV technologies is handling electronics that require low energy, such as watches, calculators, cameras, which are working well, even in normal light environments such as classrooms and offices.
- Battery Charging: Photovoltaic system provides constant and small current to the batteries to prevent discharge problems. These PV cells are very reliable and a cheap solution in these cases.
- Warning signal: PV is used to power warning signal in several areas such as the transportation, oil industries, utility and military. This warning signal that could be, highway warning signs, transmission tower, navigational beacons.
- Remote observation: the applications of photovoltaic have become very large and observation system is one of these largest applications. PV systems are used to monitor the water, weather, temperature, flow rate and oil pipes.

